Global Competence Model™
Global competence implies the ability to interact positively and effectively with anyone in the world. Our latest worldwide research study, which was concluded in 2018, updated the worldwide consensus definition of “global competence” to better represent the breadth and rigor of the original research.
Worldwide Consensus Definition of Global Competence:
Global Competence Model™
“Having flexible, respectful attitudes,
including self-perspective,
and applying knowledge of the historical, geographic, and societal factors that influence cultures
in order to effectively interact and build relationships
with people around the world.”
C. K. Hunter and W. D. Hunter, Ed.D., 2018
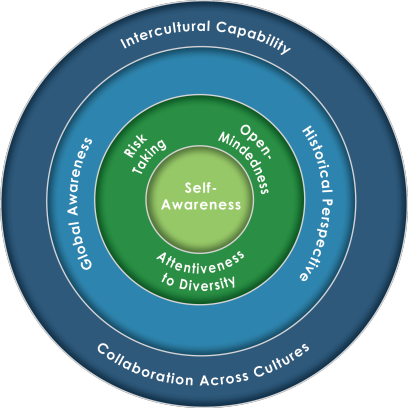
The Global Competence Model™ visually represents the specific combination of knowledge, skills, and attitudes necessary for global competence, as determined by comprehensive original worldwide consensus research. It is the unique compilation of factors, which we call “dimensions,” that jointly comprise global competence.
As a competency, by definition, requires a cluster of various capabilities, no single dimension is a competency, and the phrase “global competencies” is a misnomer. Therefore, it is the synergy of all eight dimensions that collectively comprise global competence.
.

Internal Readiness
The green sections of the model, which relate to the self-perspective and attitudinal drivers of Global Competence, denote Internal Readiness.
Beginning at the light green core is the ability to know yourself and how you fit into your own culture, including personal preference gaps compared with norms and mores (Self-Awareness).
The darker green layer reflects how you approach people and situations. Having a curiosity to learn about things holistically before arriving at conclusions (Open-Mindedness); possessing a sensitivity to and a respect for differences (Attentiveness to Diversity); and maintaining a willingness to extend beyond your cultural framework by trying new experiences (Risk Taking) are the essential and flexible attitudes identified by the research.

External Readiness
The blue sections of the model, which highlight a person’s acquired knowledge through education or life experience, represent External Readiness.
The lighter blue layer represents knowledge of major cultures around the world—both visible aspects (Global Awareness) and hidden aspects that inform values and beliefs (Historical Perspective).
The darker blue layer reflects the interpersonal skills that you develop with life experience, and your ability to apply cultural knowledge to personal interactions; thus a cultural knowledge deficiency can prevent a person from adapting empathetically. Critical skills include your ability to modify outward behavior to show respect for different cultural preferences (Intercultural Capability) and your ability to work effectively in diverse teams (Collaboration Across Cultures).
Contact Us
For More Information